Portal:Mathematics
- አማርኛ
- العربية
- Avañe'ẽ
- Авар
- تۆرکجه
- বাংলা
- 閩南語 / Bân-lâm-gú
- Беларуская (тарашкевіца)
- Bikol Central
- Български
- Català
- Cebuano
- Čeština
- الدارجة
- Deutsch
- Eesti
- Ελληνικά
- Español
- فارسی
- Français
- Gĩkũyũ
- 한국어
- Hausa
- Հայերեն
- हिन्दी
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Interlingua
- Íslenska
- Italiano
- עברית
- ქართული
- Қазақша
- Kiswahili
- Kreyòl ayisyen
- Kurdî
- Latina
- Lietuvių
- Magyar
- Македонски
- Malti
- مصرى
- ဘာသာမန်
- Bahasa Melayu
- မြန်မာဘာသာ
- Nederlands
- 日本語
- Oʻzbekcha / ўзбекча
- ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
- پښتو
- Picard
- Polski
- Português
- Română
- Runa Simi
- Русский
- Shqip
- සිංහල
- سنڌي
- Slovenčina
- Soomaaliga
- کوردی
- Српски / srpski
- Suomi
- Svenska
- தமிழ்
- Taclḥit
- Татарча / tatarça
- ၽႃႇသႃႇတႆး
- ไทย
- Тоҷикӣ
- Türkçe
- Українська
- اردو
- Tiếng Việt
- 文言
- 吴语
- ייִדיש
- Yorùbá
- 粵語
- Zazaki
- 中文
- Batak Mandailing
- ⵜⴰⵎⴰⵣⵉⵖⵜ ⵜⴰⵏⴰⵡⴰⵢⵜ
Tools
Actions
General
Print/export
In other projects
Appearance
Portal maintenance status: (December 2018)
|
Wikipedia portal for content related to Mathematics
-
Abacus, a ancient hand-operated calculating.
-
Portrait of Emmy Noether, around 1900.
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, theories and theorems that are developed and proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). (Full article...)
Featured articles
-
Image 1
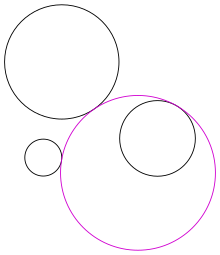
Figure 1: A solution (in purple) to Apollonius's problem. The given circles are shown in black.
In Euclidean plane geometry, Apollonius's problem is to construct circles that are tangent to three given circles in a plane (Figure 1). Apollonius of Perga (c. 262 BC – c. 190 BC) posed and solved this famous problem in his work Ἐπαφαί (Epaphaí, "Tangencies"); this work has been lost, but a 4th-century AD report of his results by Pappus of Alexandria has survived. Three given circles generically have eight different circles that are tangent to them (Figure 2), a pair of solutions for each way to divide the three given circles in two subsets (there are 4 ways to divide a set of cardinality 3 in 2 parts).
In the 16th century, Adriaan van Roomen solved the problem using intersecting hyperbolas, but this solution does not use only straightedge and compass constructions. François Viète found such a solution by exploiting limiting cases: any of the three given circles can be shrunk to zero radius (a point) or expanded to infinite radius (a line). Viète's approach, which uses simpler limiting cases to solve more complicated ones, is considered a plausible reconstruction of Apollonius' method. The method of van Roomen was simplified by Isaac Newton, who showed that Apollonius' problem is equivalent to finding a position from the differences of its distances to three known points. This has applications in navigation and positioning systems such as LORAN. (Full article...) -
Image 2
The Quine–Putnam indispensability argument is an argument in the philosophy of mathematics for the existence of abstract mathematical objects such as numbers and sets, a position known as mathematical platonism. It was named after the philosophers Willard Van Orman Quine and Hilary Putnam, and is one of the most important arguments in the philosophy of mathematics.
Although elements of the indispensability argument may have originated with thinkers such as Gottlob Frege and Kurt Gödel, Quine's development of the argument was unique for introducing to it a number of his philosophical positions such as naturalism, confirmational holism, and the criterion of ontological commitment. Putnam gave Quine's argument its first detailed formulation in his 1971 book Philosophy of Logic. He later came to disagree with various aspects of Quine's thinking, however, and formulated his own indispensability argument based on the no miracles argument in the philosophy of science. A standard form of the argument in contemporary philosophy is credited to Mark Colyvan; whilst being influenced by both Quine and Putnam, it differs in important ways from their formulations. It is presented in the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy: (Full article...) -
Image 3One of Molyneux's celestial globes, which is displayed in Middle Temple Library – from the frontispiece of the Hakluyt Society's 1889 reprint of A Learned Treatise of Globes, both Cœlestiall and Terrestriall, one of the English editions of Robert Hues' Latin work Tractatus de Globis (1594)
Emery Molyneux (/ˈɛməri ˈmɒlɪnoʊ/ EM-ər-ee MOL-in-oh; died June 1598) was an English Elizabethan maker of globes, mathematical instruments and ordnance. His terrestrial and celestial globes, first published in 1592, were the first to be made in England and the first to be made by an Englishman.
Molyneux was known as a mathematician and maker of mathematical instruments such as compasses and hourglasses. He became acquainted with many prominent men of the day, including the writer Richard Hakluyt and the mathematicians Robert Hues and Edward Wright. He also knew the explorers Thomas Cavendish, Francis Drake, Walter Raleigh and John Davis. Davis probably introduced Molyneux to his own patron, the London merchant William Sanderson, who largely financed the construction of the globes. When completed, the globes were presented to Elizabeth I. Larger globes were acquired by royalty, noblemen and academic institutions, while smaller ones were purchased as practical navigation aids for sailors and students. The globes were the first to be made in such a way that they were unaffected by the humidity at sea, and they came into general use on ships. (Full article...) -
Image 4Damage from Hurricane Katrina in 2005. Actuaries need to estimate long-term levels of such damage in order to accurately price property insurance, set appropriate reserves, and design appropriate reinsurance and capital management strategies.
An actuary is a professional with advanced mathematical skills who deals with the measurement and management of risk and uncertainty. These risks can affect both sides of the balance sheet and require asset management, liability management, and valuation skills. Actuaries provide assessments of financial security systems, with a focus on their complexity, their mathematics, and their mechanisms. The name of the corresponding academic discipline is actuarial science.
While the concept of insurance dates to antiquity, the concepts needed to scientifically measure and mitigate risks have their origins in the 17th century studies of probability and annuities. Actuaries of the 21st century require analytical skills, business knowledge, and an understanding of human behavior and information systems to design programs that manage risk, by determining if the implementation of strategies proposed for mitigating potential risks, does not exceed the expected cost of those risks actualized. The steps needed to become an actuary, including education and licensing, are specific to a given country, with various additional requirements applied by regional administrative units; however, almost all processes impart universal principles of risk assessment, statistical analysis, and risk mitigation, involving rigorously structured training and examination schedules, taking many years to complete. (Full article...) -
Image 5Elementary algebra studies which values solve equations formed using arithmetical operations.
Algebra is the branch of mathematics that studies certain abstract systems, known as algebraic structures, and the manipulation of expressions within those systems. It is a generalization of arithmetic that introduces variables and algebraic operations other than the standard arithmetic operations, such as addition and multiplication.
Elementary algebra is the main form of algebra taught in schools. It examines mathematical statements using variables for unspecified values and seeks to determine for which values the statements are true. To do so, it uses different methods of transforming equations to isolate variables. Linear algebra is a closely related field that investigates linear equations and combinations of them called systems of linear equations. It provides methods to find the values that solve all equations in the system at the same time, and to study the set of these solutions. (Full article...) -
Image 6Portrait by August Köhler, c. 1910, after 1627 original
Johannes Kepler (/ˈkɛplər/; German: [joˈhanəs ˈkɛplɐ, -nɛs -] ⓘ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws of planetary motion, and his books Astronomia nova, Harmonice Mundi, and Epitome Astronomiae Copernicanae, influencing among others Isaac Newton, providing one of the foundations for his theory of universal gravitation. The variety and impact of his work made Kepler one of the founders and fathers of modern astronomy, the scientific method, natural and modern science. He has been described as the "father of science fiction" for his novel Somnium.
Kepler was a mathematics teacher at a seminary school in Graz, where he became an associate of Prince Hans Ulrich von Eggenberg. Later he became an assistant to the astronomer Tycho Brahe in Prague, and eventually the imperial mathematician to Emperor Rudolf II and his two successors Matthias and Ferdinand II. He also taught mathematics in Linz, and was an adviser to General Wallenstein.
Additionally, he did fundamental work in the field of optics, being named the father of modern optics, in particular for his Astronomiae pars optica. He also invented an improved version of the refracting telescope, the Keplerian telescope, which became the foundation of the modern refracting telescope, while also improving on the telescope design by Galileo Galilei, who mentioned Kepler's discoveries in his work. (Full article...) -
Image 7The title page of a 1634 version of Hues' Tractatus de globis in the collection of the Biblioteca Nacional de Portugal
Robert Hues (1553 – 24 May 1632) was an English mathematician and geographer. He attended St. Mary Hall at Oxford, and graduated in 1578. Hues became interested in geography and mathematics, and studied navigation at a school set up by Walter Raleigh. During a trip to Newfoundland, he made observations which caused him to doubt the accepted published values for variations of the compass. Between 1586 and 1588, Hues travelled with Thomas Cavendish on a circumnavigation of the globe, performing astronomical observations and taking the latitudes of places they visited. Beginning in August 1591, Hues and Cavendish again set out on another circumnavigation of the globe. During the voyage, Hues made astronomical observations in the South Atlantic, and continued his observations of the variation of the compass at various latitudes and at the Equator. Cavendish died on the journey in 1592, and Hues returned to England the following year.
In 1594, Hues published his discoveries in the Latin work Tractatus de globis et eorum usu (Treatise on Globes and Their Use) which was written to explain the use of the terrestrial and celestial globes that had been made and published by Emery Molyneux in late 1592 or early 1593, and to encourage English sailors to use practical astronomical navigation. Hues' work subsequently went into at least 12 other printings in Dutch, English, French and Latin. (Full article...) -
Image 8Bust of Shen at the Beijing Ancient Observatory
Shen Kuo (Chinese: 沈括; 1031–1095) or Shen Gua, courtesy name Cunzhong (存中) and pseudonym Mengqi (now usually given as Mengxi) Weng (夢溪翁), was a Chinese polymath, scientist, and statesman of the Song dynasty (960–1279). Shen was a master in many fields of study including mathematics, optics, and horology. In his career as a civil servant, he became a finance minister, governmental state inspector, head official for the Bureau of Astronomy in the Song court, Assistant Minister of Imperial Hospitality, and also served as an academic chancellor. At court his political allegiance was to the Reformist faction known as the New Policies Group, headed by Chancellor Wang Anshi (1021–1085).
In his Dream Pool Essays or Dream Torrent Essays (夢溪筆談; Mengxi Bitan) of 1088, Shen was the first to describe the magnetic needle compass, which would be used for navigation (first described in Europe by Alexander Neckam in 1187). Shen discovered the concept of true north in terms of magnetic declination towards the north pole, with experimentation of suspended magnetic needles and "the improved meridian determined by Shen's [astronomical] measurement of the distance between the pole star and true north". This was the decisive step in human history to make compasses more useful for navigation, and may have been a concept unknown in Europe for another four hundred years (evidence of German sundials made circa 1450 show markings similar to Chinese geomancers' compasses in regard to declination). (Full article...) -
Image 9

The weighing pans of this balance scale contain zero objects, divided into two equal groups.
In mathematics, zero is an even number. In other words, its parity—the quality of an integer being even or odd—is even. This can be easily verified based on the definition of "even": zero is an integer multiple of 2, specifically 0 × 2. As a result, zero shares all the properties that characterize even numbers: for example, 0 is neighbored on both sides by odd numbers, any decimal integer has the same parity as its last digit—so, since 10 is even, 0 will be even, and if y is even then y + x has the same parity as x—indeed, 0 + x and x always have the same parity.
Zero also fits into the patterns formed by other even numbers. The parity rules of arithmetic, such as even − even = even, require 0 to be even. Zero is the additive identity element of the group of even integers, and it is the starting case from which other even natural numbers are recursively defined. Applications of this recursion from graph theory to computational geometry rely on zero being even. Not only is 0 divisible by 2, it is divisible by every power of 2, which is relevant to the binary numeral system used by computers. In this sense, 0 is the "most even" number of all. (Full article...) -
Image 10

Émile Michel Hyacinthe Lemoine (French: [emil ləmwan]; 22 November 1840 – 21 February 1912) was a French civil engineer and a mathematician, a geometer in particular. He was educated at a variety of institutions, including the Prytanée National Militaire and, most notably, the École Polytechnique. Lemoine taught as a private tutor for a short period after his graduation from the latter school.
Lemoine is best known for his proof of the existence of the Lemoine point (or the symmedian point) of a triangle. Other mathematical work includes a system he called Géométrographie and a method which related algebraic expressions to geometric objects. He has been called a co-founder of modern triangle geometry, as many of its characteristics are present in his work. (Full article...) -
Image 11The number π (/paɪ/ ⓘ; spelled out as "pi") is a mathematical constant, approximately equal to 3.14159, that is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. It appears in many formulae across mathematics and physics, and some of these formulae are commonly used for defining π, to avoid relying on the definition of the length of a curve.
The number π is an irrational number, meaning that it cannot be expressed exactly as a ratio of two integers, although fractions such asare commonly used to approximate it. Consequently, its decimal representation never ends, nor enters a permanently repeating pattern. It is a transcendental number, meaning that it cannot be a solution of an algebraic equation involving only finite sums, products, powers, and integers. The transcendence of π implies that it is impossible to solve the ancient challenge of squaring the circle with a compass and straightedge. The decimal digits of π appear to be randomly distributed, but no proof of this conjecture has been found. (Full article...)
-
Image 12

Richard Phillips Feynman (/ˈfaɪnmən/; May 11, 1918 – February 15, 1988) was an American theoretical physicist. He is best known for his work in the path integral formulation of quantum mechanics, the theory of quantum electrodynamics, the physics of the superfluidity of supercooled liquid helium, and in particle physics, for which he proposed the parton model. For his contributions to the development of quantum electrodynamics, Feynman received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965 jointly with Julian Schwinger and Shin'ichirō Tomonaga.
Feynman developed a widely used pictorial representation scheme for the mathematical expressions describing the behavior of subatomic particles, which later became known as Feynman diagrams. During his lifetime, Feynman became one of the best-known scientists in the world. In a 1999 poll of 130 leading physicists worldwide by the British journal Physics World, he was ranked the seventh-greatest physicist of all time. (Full article...) -
Image 13
Marian Adam Rejewski (Polish: [ˈmarjan rɛˈjɛfskʲi] ⓘ; 16 August 1905 – 13 February 1980) was a Polish mathematician and cryptologist who in late 1932 reconstructed the sight-unseen German military Enigma cipher machine, aided by limited documents obtained by French military intelligence.
Over the next nearly seven years, Rejewski and fellow mathematician-cryptologists Jerzy Różycki and Henryk Zygalski, working at the Polish General Staff's Cipher Bureau, developed techniques and equipment for decrypting the Enigma ciphers, even as the Germans introduced modifications to their Enigma machines and encryption procedures. Rejewski's contributions included the cryptologic card catalog and the cryptologic bomb. (Full article...) -
Image 14
Amalie Emmy Noether (US: /ˈnʌtər/, UK: /ˈnɜːtə/; German: [ˈnøːtɐ]; 23 March 1882 – 14 April 1935) was a German mathematician who made many important contributions to abstract algebra. She proved Noether's first and second theorems, which are fundamental in mathematical physics. She was described by Pavel Alexandrov, Albert Einstein, Jean Dieudonné, Hermann Weyl and Norbert Wiener as the most important woman in the history of mathematics. As one of the leading mathematicians of her time, she developed theories of rings, fields, and algebras. In physics, Noether's theorem explains the connection between symmetry and conservation laws.
Noether was born to a Jewish family in the Franconian town of Erlangen; her father was the mathematician Max Noether. She originally planned to teach French and English after passing the required examinations but instead studied mathematics at the University of Erlangen, where her father lectured. After completing her doctorate in 1907 under the supervision of Paul Gordan, she worked at the Mathematical Institute of Erlangen without pay for seven years. At the time, women were largely excluded from academic positions. In 1915, she was invited by David Hilbert and Felix Klein to join the mathematics department at the University of Göttingen, a world-renowned center of mathematical research. The philosophical faculty objected, however, and she spent four years lecturing under Hilbert's name. Her habilitation was approved in 1919, allowing her to obtain the rank of Privatdozent. (Full article...) -
Image 15In algebraic geometry and theoretical physics, mirror symmetry is a relationship between geometric objects called Calabi–Yau manifolds. The term refers to a situation where two Calabi–Yau manifolds look very different geometrically but are nevertheless equivalent when employed as extra dimensions of string theory.
Early cases of mirror symmetry were discovered by physicists. Mathematicians became interested in this relationship around 1990 when Philip Candelas, Xenia de la Ossa, Paul Green, and Linda Parkes showed that it could be used as a tool in enumerative geometry, a branch of mathematics concerned with counting the number of solutions to geometric questions. Candelas and his collaborators showed that mirror symmetry could be used to count rational curves on a Calabi–Yau manifold, thus solving a longstanding problem. Although the original approach to mirror symmetry was based on physical ideas that were not understood in a mathematically precise way, some of its mathematical predictions have since been proven rigorously. (Full article...)
Good articles
-
Image 1Donkey Kong Jr. Math is an edutainment platform video game developed and published by Nintendo for the Nintendo Entertainment System. It is a spin-off of the 1982 arcade game Donkey Kong Jr. In the game, players control Donkey Kong Jr. as he solves math problems set up by his father Donkey Kong. It was released in Japan in 1983 for the Family Computer, and in North America and the PAL region in 1986.
It is the only game in the Education Series of NES games in North America, owing to the game's lack of success. It was made available in various forms, including in the 2002 GameCube video game Animal Crossing and on the Virtual Console services for Wii and Wii U in 2007 and 2014 respectively, and in 2024 for the Nintendo Switch Online service. Donkey Kong Jr. Math was a critical and commercial failure. It has received criticism from several publications including IGN staff, who called it one of the worst Virtual Console games. (Full article...) -
Image 2Advanced Placement (AP) Statistics (also known as AP Stats) is a college-level high school statistics course offered in the United States through the College Board's Advanced Placement program. This course is equivalent to a one semester, non-calculus-based introductory college statistics course and is normally offered to sophomores, juniors and seniors in high school.
One of the College Board's more recent additions, the AP Statistics exam was first administered in May 1996 to supplement the AP program's math offerings, which had previously consisted of only AP Calculus AB and BC. In the United States, enrollment in AP Statistics classes has increased at a higher rate than in any other AP class. (Full article...) -
Image 3

The square root of 2 is equal to the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs of length 1 and is therefore a constructible number
In geometry and algebra, a real numberis constructible if and only if, given a line segment of unit length, a line segment of length
can be constructed with compass and straightedge in a finite number of steps. Equivalently,
is constructible if and only if there is a closed-form expression for
using only integers and the operations for addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and square roots.
The geometric definition of constructible numbers motivates a corresponding definition of constructible points, which can again be described either geometrically or algebraically. A point is constructible if it can be produced as one of the points of a compass and straightedge construction (an endpoint of a line segment or crossing point of two lines or circles), starting from a given unit length segment. Alternatively and equivalently, taking the two endpoints of the given segment to be the points (0, 0) and (1, 0) of a Cartesian coordinate system, a point is constructible if and only if its Cartesian coordinates are both constructible numbers.[1] Constructible numbers and points have also been called ruler and compass numbers and ruler and compass points, to distinguish them from numbers and points that may be constructed using other processes. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Numbers written with Cistercian numerals. From left to right: 1 in units place, 2 in tens place (20), 3 in hundreds place (300), 4 in thousands place (4,000), then compound numbers 5,555, 6,789, 9,394.
The medieval Cistercian numerals, or "ciphers" in nineteenth-century parlance, were developed by the Cistercian monastic order in the early thirteenth century at about the time that Arabic numerals were introduced to northwestern Europe. They are more compact than Arabic or Roman numerals, with a single glyph able to indicate any integer from 1 to 9,999.
Digits are based on a horizontal or vertical stave, with the position of the digit on the stave indicating its place value (units, tens, hundreds or thousands). These digits are compounded on a single stave to indicate more complex numbers. The Cistercians eventually abandoned the system in favor of the Arabic numerals, but marginal use outside the order continued until the early twentieth century. (Full article...) -
Image 5In geometry, the Beckman–Quarles theorem states that if a transformation of the Euclidean plane or a higher-dimensional Euclidean space preserves unit distances, then it preserves all Euclidean distances. Equivalently, every homomorphism from the unit distance graph of the plane to itself must be an isometry of the plane. The theorem is named after Frank S. Beckman and Donald A. Quarles Jr., who published this result in 1953; it was later rediscovered by other authors and re-proved in multiple ways. Analogous theorems for rational subsets of Euclidean spaces, or for non-Euclidean geometry, are also known. (Full article...)
-
Image 6

Selected witch of Agnesi curves (green), and the circles they are constructed from (blue), with radius parameters ,
,
, and
.
In mathematics, the witch of Agnesi (Italian pronunciation: [aɲˈɲeːzi, -eːsi; -ɛːzi]) is a cubic plane curve defined from two diametrically opposite points of a circle.
The curve was studied as early as 1653 by Pierre de Fermat, in 1703 by Guido Grandi, and by Isaac Newton. It gets its name from Italian mathematician Maria Gaetana Agnesi who published it in 1748. The Italian name la versiera di Agnesi is based on Latin versoria (sheet of sailing ships) and the sinus versus.
This was read by John Colson as l’avversiera di Agnesi, where avversiera is translated as "woman who is against God" and interpreted as "witch". (Full article...) -
Image 7

The boundary of a Reuleaux triangle is a constant width curve based on an equilateral triangle. All points on a side are equidistant from the opposite vertex.
A Reuleaux triangle [ʁœlo] is a curved triangle with constant width, the simplest and best known curve of constant width other than the circle. It is formed from the intersection of three circular disks, each having its center on the boundary of the other two. Constant width means that the separation of every two parallel supporting lines is the same, independent of their orientation. Because its width is constant, the Reuleaux triangle is one answer to the question "Other than a circle, what shape can a manhole cover be made so that it cannot fall down through the hole?"
They are named after Franz Reuleaux, a 19th-century German engineer who pioneered the study of machines for translating one type of motion into another, and who used Reuleaux triangles in his designs. However, these shapes were known before his time, for instance by the designers of Gothic church windows, by Leonardo da Vinci, who used it for a map projection, and by Leonhard Euler in his study of constant-width shapes. Other applications of the Reuleaux triangle include giving the shape to guitar picks, fire hydrant nuts, pencils, and drill bits for drilling filleted square holes, as well as in graphic design in the shapes of some signs and corporate logos. (Full article...) -
Image 8
Andrew Mattei Gleason (1921–2008) was an American mathematician who made fundamental contributions to widely varied areas of mathematics, including the solution of Hilbert's fifth problem, and was a leader in reform and innovation in mathematics teaching at all levels. Gleason's theorem in quantum logic and the Greenwood–Gleason graph, an important example in Ramsey theory, are named for him.
As a young World War II naval officer, Gleason broke German and Japanese military codes. After the war he spent his entire academic career at Harvard University, from which he retired in 1992. His numerous academic and scholarly leadership posts included chairmanship of the Harvard Mathematics Department and the Harvard Society of Fellows, and presidency of the American Mathematical Society. He continued to advise the United States government on cryptographic security, and the Commonwealth of Massachusetts on mathematics education for children, almost until the end of his life. (Full article...) -
Image 9
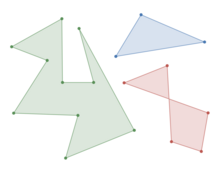
Two simple polygons (green and blue) and a self-intersecting polygon (red, in the lower right, not simple)
In geometry, a simple polygon is a polygon that does not intersect itself and has no holes. That is, it is a piecewise-linear Jordan curve consisting of finitely many line segments. These polygons include as special cases the convex polygons, star-shaped polygons, and monotone polygons.
The sum of external angles of a simple polygon is. Every simple polygon with
sides can be triangulated by
of its diagonals, and by the art gallery theorem its interior is visible from some
of its vertices. (Full article...)
-
Image 10
Maurits Cornelis Escher (/ˈɛʃər/; Dutch: [ˈmʌurɪts kɔrˈneːlɪs ˈɛɕər]; 17 June 1898 – 27 March 1972) was a Dutch graphic artist who made woodcuts, lithographs, and mezzotints, many of which were inspired by mathematics.
Despite wide popular interest, for most of his life Escher was neglected in the art world, even in his native Netherlands. He was 70 before a retrospective exhibition was held. In the late twentieth century, he became more widely appreciated, and in the twenty-first century he has been celebrated in exhibitions around the world.
His work features mathematical objects and operations including impossible objects, explorations of infinity, reflection, symmetry, perspective, truncated and stellated polyhedra, hyperbolic geometry, and tessellations. Although Escher believed he had no mathematical ability, he interacted with the mathematicians George Pólya, Roger Penrose, and Donald Coxeter, and the crystallographer Friedrich Haag, and conducted his own research into tessellation. (Full article...) -
Image 11In mathematics, the harmonic series is the infinite series formed by summing all positive unit fractions:
The firstterms of the series sum to approximately
, where
is the natural logarithm and
is the Euler–Mascheroni constant. Because the logarithm has arbitrarily large values, the harmonic series does not have a finite limit: it is a divergent series. Its divergence was proven in the 14th century by Nicole Oresme using a precursor to the Cauchy condensation test for the convergence of infinite series. It can also be proven to diverge by comparing the sum to an integral, according to the integral test for convergence. (Full article...)
-
Image 12In mathematics, the three-gap theorem, three-distance theorem, or Steinhaus conjecture states that if one places n points on a circle, at angles of θ, 2θ, 3θ, ... from the starting point, then there will be at most three distinct distances between pairs of points in adjacent positions around the circle. When there are three distances, the largest of the three always equals the sum of the other two. Unless θ is a rational multiple of π, there will also be at least two distinct distances.
This result was conjectured by Hugo Steinhaus, and proved in the 1950s by Vera T. Sós, János Surányi [hu], and Stanisław Świerczkowski; more proofs were added by others later. Applications of the three-gap theorem include the study of plant growth and musical tuning systems, and the theory of light reflection within a mirrored square. (Full article...)
Did you know
- ... that after Archimedes first defined convex curves, mathematicians lost interest in their analysis until the 19th century, more than two millennia later?
- ... that two members of the French parliament were killed when a delayed-action German bomb exploded in the town hall at Bapaume on 25 March 1917?
- ... that Latvian-Soviet artist Karlis Johansons exhibited a skeletal tensegrity form of the Schönhardt polyhedron seven years before Erich Schönhardt's 1928 paper on its mathematics?
- ... that the word algebra is derived from an Arabic term for the surgical treatment of bonesetting?
- ... that people in Madagascar perform algebra on tree seeds in order to tell the future?
- ... that despite a mathematical model deeming the ice cream bar flavour Goody Goody Gum Drops impossible, it was still created?
- ... that Fairleigh Dickinson's upset victory over Purdue was the biggest upset in terms of point spread in NCAA tournament history, with Purdue being a 23+1⁄2-point favorite?
- ... that subgroup distortion theory, introduced by Misha Gromov in 1993, can help encode text?

- ...that the Rule 184 cellular automaton can simultaneously model the behavior of cars moving in traffic, the accumulation of particles on a surface, and particle-antiparticle annihilation reactions?
- ...that a cyclic cellular automaton is a system of simple mathematical rules that can generate complex patterns mixing random chaos, blocks of color, and spirals?
- ...that a nonconvex polygon with three convex vertices is called a pseudotriangle?
- ...that the axiom of choice is logically independent of the other axioms of Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory?
- ...that the Pythagorean Theorem generalizes to any three similar shapes on the three sides of a right-angled triangle?
- ...that the orthocenter, circumcenter, centroid and the centre of the nine-point circle all lie on one line, the Euler line?
- ...that an arbitrary quadrilateral will tessellate?
Showing 7 items out of 75
Featured pictures
-
Image 2Mandelbrot set, step 14, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 4Hypotrochoid, by Sam Derbyshire (edited by Anevrisme and Perhelion) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 5Mandelbrot set, start, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 7Mandelbrot set, step 7, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 9Desargues' theorem, by Dynablast (edited by Jujutacular and Julia W) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 10Mandelbrot set, step 2, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 11Mandelbrot set, step 10, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 12Fields Medal, front, by Stefan Zachow (edited by King of Hearts) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 13Lorenz attractor at Chaos theory, by Wikimol (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 14Mandelbrot set, step 11, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 17Mandelbrot set, step 1, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 19Mandelbrot set, step 6, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 20Mandelbrot set, step 8, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 21Mandelbrot set, step 13, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 22Mandelbrot set, step 3, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 23Proof of the Pythagorean theorem, by Joaquim Alves Gaspar (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 24Fields Medal, back, by Stefan Zachow (edited by King of Hearts) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 25Mandelbrot set, step 5, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 26Line integral of scalar field, by Lucas V. Barbosa (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 27Mandelbrot set, by Simpsons contributor (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 28Tetrahedral group at Symmetry group, by Debivort (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 30Mandelbrot set, step 12, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 31Mandelbrot set, step 4, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 32Mandelbrot set, step 9, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 33Anscombe's quartet, by Schutz (edited by Avenue) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 34Cellular automata at Reflector (cellular automaton), by Simpsons contributor (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
Get involved
- For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Mathematics-related articles, visit WikiProject Mathematics.
Categories
Topics
Index of articles
| ARTICLE INDEX: | |
| MATHEMATICIANS: |
Vital articles
- » subpages: Level 4 Mathematics articles, Level 5 Mathematics articles
Discover Wikipedia using portals
- ^ Kazarinoff (2003), pp. 10, 15 sfnmp error: no target: CITEREFKazarinoff2003 (help); Martin (1998), p. 41, Corollary 2.16 sfnmp error: no target: CITEREFMartin1998 (help).
Hidden categories:
- Pages using the Phonos extension
- Pages with German IPA
- Pages including recorded pronunciations
- Pages with French IPA
- Pages with Polish IPA
- Pages with Italian IPA
- Pages with Dutch IPA
- Wikipedia semi-protected portals
- Manually maintained portal pages from December 2018
- All manually maintained portal pages
- Portals with triaged subpages from December 2018
- All portals with triaged subpages
- Portals with named maintainer
- Wikipedia move-protected portals
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 31–40 articles in article list
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 101–200 articles in article list
- Random portal component with over 50 available subpages